Blockchain Technology — What is It and How Does It Work
Now, in almost any company of people, a conversation about cryptocurrency can arise. In most cases, the topics of conversation are the following: Bitcoin price spikes, enrichment of the “lucky ones”, price manipulation, as well as the prospects for this market. However, often even cryptocurrency traders have a vague idea of how everything works inside and how this ecosystem works. And the term “blockchain” is used as a magic spell and is a kind of “black box”.
Blockchain promises to become one of the basic components of the Internet of the future. This technology has already significantly influenced our lives and is not going to stop there.
After reading this article, you are unlikely to be able to create your own cryptocurrency or program a smart contract on the Ethereum network. However, there is every chance that the words “blockchain”, “mining”, “cryptocurrency”, “hash” will no longer cause a restrained “understanding” nod and an acute desire to change the subject. Let's understand what is blockchain in simple words.
A bit of history
In 2008, a certain Satoshi Nakamoto published a document “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” online. Already in 2009, Satoshi implemented the Bitcoin cryptocurrency blockchain, which became the starting point for the development of the crypto market. It is still unknown who is hiding under the name of the founder of the first blockchain system — a lone genius or a group of people. A sufficient number of investigations have already been carried out on this subject, and new contenders for this such a significant role regularly appear.
“Peer-to-Peer” is not in vain in the title of Satoshi Nakamoto's document. P2P network is a decentralized complex of computers. In such a system, as a rule, each participant (computer, node) can play the role of both a client and a server. In other words, the network operates without a distinct leader (dedicated server) and the loss of any of the participants (or a group of participants) does not affect the performance of the entire complex. The principle of decentralization has become one of the fundamental principles for blockchain technology.
The creation of infrastructure for Bitcoin launched an entire industry. More and more new implementations of blockchain technology began to appear. In 2015, the Ethereum network was launched, the ideological inspirer of which is the programmer Vitalik Buterin. The Ethereum blockchain has become a platform for the Ether cryptocurrency, which occupies a confident second place in terms of capitalization after Bitcoin. However, the Ethereum blockchain is interesting not only as a platform for the second most influential cryptocurrency in the world. The Ethereum network is positioned as an effective tool and workspace for the creation and implementation of so-called “smart contracts” and decentralized online services.

Blockchain is an open source technology. This means that anyone with proper technical training can use existing developments to create their own product. At the moment, there are already thousands of different cryptocurrencies. And their number is likely to grow rapidly.
How to create your own blockchain network? Not so long ago, IBM presented the “Blockchain as a Service” service based on the Hyperledger Fabric open-source project. This tool allows clients to create their own blockchain networks and use them for various business tasks.
What is Blockchain
Blockchain is a shared database that stores transaction information and other ledger entries. Among the main principles of technology are the following:
- decentralization;
- data immutability;
- cryptographic protection.
Decentralization is ensured by the presence of copies of the blockchain with all information about previously conducted transactions on all nodes of the network. Data is stored in blocks that line up in a chain.
In the blockchain network, transactions cannot be changed or deleted. You can only add new ones. The immutability of data allows you to ensure the protection of transactions performed. It is extremely difficult for fraudsters to make changes to the blockchain blocks and, for example, rewrite the conditions of a particular transaction.
How blocks are connected
Data protection in the block chain is ensured by cryptographic hash functions. Different blockchains may have different protocols, encryption nuances, and principles for forming links. A blockchain platform is a complex structure with high-level encryption and different sets of protection mechanisms. We will consider the basic principles of cryptographic data protection.
First you need to understand what a cryptographic hash function is. This is such a function that takes certain data as input, processes it and produces some kind of string. In this case, several rules must be followed:
- the result of the transformation is always the same for the same set of input data;
- any changes to the input also change the hash sum of the output, and this process is unpredictable;
- the function works only in one direction (it is impossible to recreate the original data array using the hash code);
- collision resistance (the inability to pick up two different lists of input data that would end up with the same hash code).
Why is a hash function needed in a blockchain network at all? Thanks to this mechanism, each block receives its own unique identifier. The input is the data of a particular block (information about transactions, changes in the registry, etc.), and the output is a hash code of this block, which is a kind of “fingerprint”.
- Automate the work of an online store or landing
- Empower through integration
- Don't spend money on programmers and integrators
- Save time by automating routine tasks
But simply assigning a unique identifier to a data block is not enough. The peculiarity of the blockchain is that each segment has a cryptographic pointer to the previous one. The block hash sum is passed to the next block and thus influences its “fingerprint”. Due to this, an immutable chain of records is created. If you make changes in the block (for example, change the addressee of the transaction), then the hash code will no longer correspond to the value accepted by everyone. At the same time, it must be remembered that copies of the blockchain are stored on other network nodes. Therefore, any discrepancy between the hash code and the entries in the original chain is easy to trace. Such a "bad" block is simply ignored.
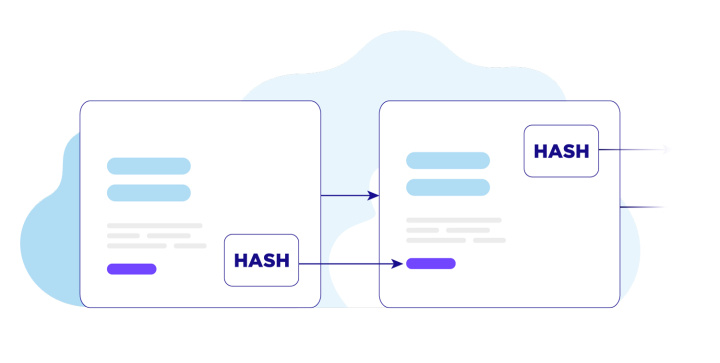
There is a rule in the blokchain system — the longest sequence of blocks is taken as the original chain. If “dishonest” participants want to make changes in one of the blocks, then they will have to change all subsequent blocks and build a chain longer than the existing one. This task is feasible only in theory. For example, if one of the participants in the system has more than 50% of the computing power of the entire network.
How Blockchain works
What is blockchain mining? The blocks in the blockchain are formed by the so-called miners — these are active participants in the network, which support the operation of the chain. Consider the key steps:
- A transaction is created in the blockchain network (while it has not yet been fixed);
- Miners collect a complex of uncommitted transactions into a block and try to create a “correct” hash code (for which special conditions are defined);
- If a valid hash sum is not obtained at the output, another set of transactions is collected and the calculations are carried out again;
- If the hash satisfies the necessary conditions, the miner notifies other participants in the “race for the hash” about this;
- Other miners check the work of the “lucky” colleague, and if it passes the check, the block is added to the network, blockchain transactions are fixed.
Such a chain of events is a simplified interpretation of the functioning of the blockchain. There are quite a few nuances to mining, transaction validation, and block building processes.
For creating new links in the chain, miners are rewarded in the form of the internal digital currency of the blockchain. The result of all efforts depends on the computing power devoted to finding a valid hash sum. Also, the priority of building blocks can be regulated by the internal rules of the network. For example, preference is given to participants with a large number of "coins" in the account.
Decentralized networks — getting rid of intermediaries
Blockchain is, in simple terms, a distributed database. Information is duplicated and stored on thousands of computers. Data belongs to everyone and belongs to no one. There is no computer, organization, person or group of people on which the operation of the blockchain depends. Although there are a few caveats here:
- if there is a person or company that has more than 50% of the network capacity, then it is quite possible to influence it;
- the rules for the functioning of the blockchain may imply an increased priority for the creation of blocks for certain participants in the network, which reduces the degree of decentralization.
Nevertheless, the blockchain is an effective implementation of distributed information storage, where it is difficult to find a place for a monopolist-holder of data or an administrator-moderator.
Blockchain is a tool that allows you to implement the exchange of value without a third party. When it comes to the benefits of technology for the average user, as a rule, the first or second advantage is getting rid of intermediaries in money transfers.
When we send money to each other, we use the services of a bank or a payment system. This third party stores information about us and our accounts. In fact, the work of an intermediary during the execution of a transaction consists in checking the data and correcting the records in the database. To exaggerate, in the column of available money, a number is taken away from user X, and in the column of user Y, they are added. The process of reconciliation of data and changes in the registry can take quite a lot of time.
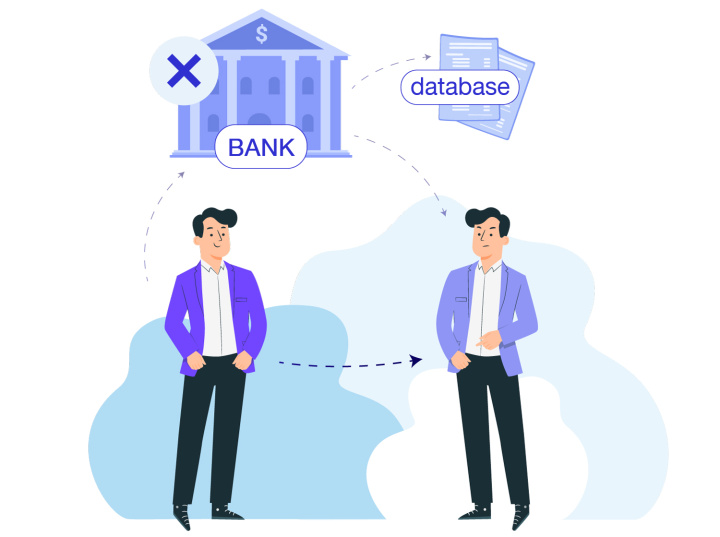
How does cryptocurrency work? This is the internal currency of the blockchain. The system provides a high speed of digital asset transfer. In addition, there is no need for mediation. The validity of the operation is controlled by all network participants and there is no single server/organization/user on which the transaction process depends.
How good is a system without intermediaries? Clients of a bank or payment system are completely dependent on these organizations. A person's account can be blocked for any reason, an attack can be made on the server with data, etc. Each of these unpleasant cases “cuts off” the user from his property. In the blockchain, there is no computer or group of machines that can be hacked and stop the system.
The decentralized database makes it possible to exclude a third party in the regulation of the exchange of values. However, there are different points of view on this matter. On the one hand, this is an opportunity to build a monetary system without the control of the state, corporations, etc. On the other hand, an uncontrolled field is a good tool for storing and exchanging valuables obtained by illegal methods.
Perspectives of Blockchain technology
Considering the trillion (in dollars) capitalization of the cryptocurrency market, it is safe to say that blockchain technology has already changed the world. However, digital money is far from the only implementation of the distributed ledger capabilities. On the basis of blockchain technology, a new format of the Internet is already being created — the Internet of Values. You can link real estate, stocks, paintings, music, digital art, etc. to a digital record.
Smart contracts written on the blockchain platform make it easier to solve various business problems. A distributed network can also allow organizing the voting process with minimal chances of fraud and other external interference. On the basis of the blockchain, NFT tokens, NFT games and much more have appeared, which in the recent past did not fit into the usual picture of the world. So, with all the controversial and ambiguous moments, it’s worth getting used to the fact that the blockchain is with us seriously and for a long time.
Apix-Drive is a simple and efficient system connector that will help you automate routine tasks and optimize business processes. You can save time and money, direct these resources to more important purposes. Test ApiX-Drive and make sure that this tool will relieve your employees and after 5 minutes of settings your business will start working faster.


