SaaS, PaaS, and Other _aaS – What is It, How are They Different and Where are They Used
When people today habitually use some convenient service from the SaaS category, they are unlikely to think about the history of its occurrence. But such information improves understanding of how these programs work, and, accordingly, makes it easier to work with them. In our article, we will take a detailed look at what SaaS, PaaS, and other XaaS are.
What is a Cloud
The word "cloud" in the IT field appeared in the 1990s and had an entirely different meaning. They then called the Internet, to
convey in a figurative form what it is – a boundless network with
rapidly changing components.
The “cloud” entered info communication technologies in 2006: the American company Amazon pleased its customers with a novelty – the Elastic Computing Cloud service, and Eric Schmidt, CEO of Google, used the terms “cloud” and “cloud computing” in one of his reports. Clouds were then called computing systems of various types, which provided users with remote shared access to resources at their request.
Since that time, the explanation of the term "cloud" has been clarified many times. It was specified in 2011 by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology, USA) in its publication “The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing”:
“Cloud computing is a model that provides global, on-demand, convenient network access to a common pool of computing system resources (services, programs, networks, data storage, servers) that can be quickly provisioned, launched, and configured with a minimum of effort to manage or contact the supplier service". In addition, the publication identified 5 important qualities that every cloud should have.

History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
According to various sources, the first cloud technologies in the IT field appeared in the 1950s. At that time, the excessively high cost of computers prompted scientists to the idea of using one electronic computer at once by several employees of the company. The idea of being able to connect many users to a single processor was first voiced in 1954, but it was only in 1959 that they began to translate it into reality. The result of the hard work of scientists was the commercially successful family of computers of the "mainframe" class System/360, released by IBM in 1964. It was then that computing power began to be seen as a resource.
In 1961, American computer scientist and author of the term "artificial intelligence" John McCarthy may have first expressed the idea of cloud computing. At an MIT 100th anniversary event, he publicly announced that computing could be rented and paid for in the same way that we pay utility bills.
In 1969, on behalf of the US Department of Defense and thanks to
several scientific institutions, the ARPANET was launched. The project
was based on the idea of the American scientist Joseph Licklider. It was
to provide all people located in different parts of the world with
communication with each other, as well as access to information and
programs from any geographical point. To achieve this, computers located in
different places were united through a loosely connected network.
The next harbinger of the emergence of clouds were virtual systems that did not depend on a specific personal computer and made it possible to start work and finish it at any time. A commercial solution based on this technology was released in 1972 by IBM – it was the VM/370 operating system.
A significant moment in the history of the development of cloud services is the founding in March 1999 of the American company Salesforce.com, which developed the CRM system of the same name. Its specialists own the concept, which consists in providing users with corporate software through an ordinary website. It allowed to significantly improve the quality and efficiency of interaction with customers, and also gave large companies the opportunity to provide access to their services via the Internet.
At the very beginning of the 21st century, cloud technologies began to designate SaaS services (it stands for "software as a service"). In 2002, the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud solution platform was launched. Thanks to it, users have access to the necessary computing power and services through a browser from any device connected to the Internet.
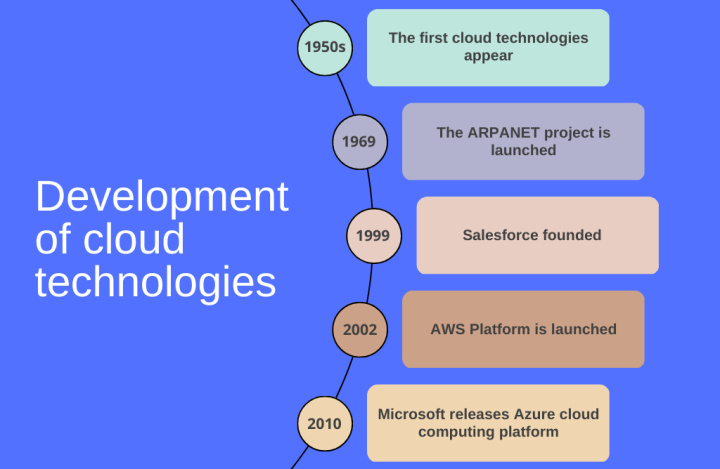
Another important date in the history of cloud technologies is 2006. It is believed that this period was the peak of Web 2.0 development because it was at this time that Google launched its cloud software package for organizations – Google Apps for Your Domain.
In 2008, Intel, Hewlett Packard and Yahoo founded the Cloud Computing Test Bed, a joint cloud computing research lab. In this "workshop" technology was honed, and new functions were created for more convenient and efficient use of clouds.
In 2010, Microsoft released its cloud computing service, Azure. Thus, a new PaaS model was introduced – “platform as a service”. It expanded the range and functionality of the company's typical cloud infrastructure, and allowed it to be combined with other Microsoft products.
The development of hardware (growth in the volume of information storage devices, the emergence of multicore processors), as well as virtualization technologies (in particular, software for creating infrastructure in a virtual environment) not only gave another impetus to the development of cloud computing, but also made them more accessible. Today, almost everyone can use them or hire a node.js developer that will make it done.
SaaS – What is It, Where is It Used, Advantages and Disadvantages
The SaaS (software as a service) market has shown high activity and
rapid development recently. Experts believe that this trend
should continue. According to Fortune Business Insights, the SaaS market
will cross the $700 billion mark by 2028.
What is SaaS
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) is a subscription software implementation model. This is a way to buy software without the need for physical installation of the program and its support on the client side. What is SaaS company? A SaaS company produces a product and hosts it on its own (or rented) servers. It deals with software support, security, and other technical nuances.
To use the SaaS product, the user only needs to pay for a subscription and go to the browser. The client gets quick and easy access to the interface and functionality of the program from almost any device connected to the Internet.
Where SaaS is Used
Cloud technologies and, in particular, the SaaS segment is actively developing and covering more and more areas of application. However, there are a few main ones:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM);
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP);
- Software products for accounting;
- Project management, communication;
- Online marketing solutions;
- BI and analytics;
- Content creation tools.
In fact, it is already quite difficult to find a niche related to digital or online activities that would not include SaaS representatives. Cloud services currently help to solve both individual tasks of self-organization and storage of files, and provide complex business processes in large enterprises.
We have already mentioned that the emergence of Salesforce.com was one of the milestones in the development of cloud technologies. The platform provides an opportunity to automate various business processes and develop customized solutions. At the same time, CRM functionality remains the most important component of the platform. Salesforce is one of the best CRM solutions on G2.com.
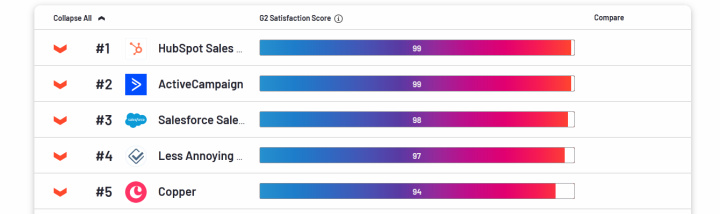
Source: G2.com
The SaaS model also provides more specialized products. For example, services such as ours. ApiX-Drive and other representatives of the integration and automation solutions market work on a subscription basis. To connect various applications, set up simple integrations or complex automated chains, all you need is a paid package, a browser, and an Internet connection.
Benefits of SaaS Solutions
The popularity of the SaaS market is obviously caused by a whole set of advantages that characterize this approach to software distribution. Let's look at the main ones:
- Simplification of the use of software for the user (without installation and self-maintenance);
- Quick and constant access to the service from any device connected to the Internet;
- Convenient and fast software distribution option (increases the company's profitability and sales level);
- The ability to quickly scale, adapting to current needs;
- Automatic software updates;
- Low requirements for end user equipment;
- Flexible payment system.
There are many obvious advantages both for buyers/users and for companies that develop software.
Disadvantages of the SaaS Model
Let's try to flip the SaaS medal and look at the negative sides of the Software as a Service model. They are. For example:
- The process of quality control of an IT product becomes more complicated (especially with active scaling);
- There may be problems with the organization of data security;
- Web application performance may be inferior to local versions;
- There are a huge number of SaaS startups on the market, not all of which can withstand competition.
Nevertheless, the SaaS market is growing and almost every one of us has come across cloud applications and tools in one way or another. Here are some popular services that are implemented under the SaaS model. You will probably find familiar names there.

PaaS – Where is It Used, Popular Providers
PaaS (Platform as a service) is a development environment that allows you to create and maintain various applications and software products in the cloud. This is a more specific service than SaaS solutions (which are essentially ready-made services for the end user). PaaS includes the infrastructure and tool set for building cloud applications. Clients get at their disposal all the necessary functionality to implement the application life cycle and its support: servers, software, databases, runtime environment, tools for deployment, testing, etc.
PaaS is a service designed for organizations and developers who want to create their own cloud solution. At the same time, the basic tasks of maintaining and ensuring the operation of the program remain with the provider. We can say that users of PaaS solutions get additional rights and tools to work in the cloud infrastructure, which allows them to independently develop and manage web applications.
Main advantages of PaaS:
- Quick start for application development;
- High level of scalability;
- Possibility of relatively simple application migration;
- Reducing the cost of producing a cloud solution;
- Reducing the application development cycle;
- Ensuring a stable level of control and security.
Popular PaaS providers
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
A platform from Amazon that provides an infrastructure for deploying web applications for various tasks. This PaaS solution supports popular programming languages and web servers (Java, Python, .NET, PHP, Go, Ruby, Apache, Nginx, etc.). Elastic Beanstalk automatically distributes the load, scales and monitors the health of the application.
Google App Engine
Google's solution for creating cloud software products. The platform
officially supports a number of the most popular programming languages.
In addition, using containers, users can use their language,
libraries, and a customized technology stack.
Microsoft Azure Pipelines
Microsoft Azure is a family of solutions delivered according to the PaaS model. Microsoft Azure Pipelines is a service for building and managing cloud applications. The platform provides parallel launch of the product on Windows, Linux, macOS. You can develop applications for iOS and Android. Popular programming languages are supported.
IBM Cloud
The IBM Cloud has two main services that are provided as PaaS. IBM Red Hat OpenShift is a service for developing and deploying applications. Also used to scale workloads and provide automatic updates. IBM Cloud Pak for Applications is an out-of-the-box application service that helps you optimize and modernize your software product.
Heroku
Heroku is a popular containerized PaaS environment. This solution allows you to run applications in smart containers that are managed by the provider. The Heroku platform supports technologies such as PostrgeSQL, MongoDB, New Relic, Searchify, MySQL, Papertrail, and more. Also, users of the Heroku development environment can integrate with the GitHub web service.
IaaS – Infrastructure Rental in the Cloud
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) – services that offer computing power, storage, and network resources. All this functionality is provided in the cloud by subscription. In the case of using an IaaS solution, organizations and developers independently manage the software, operating system, runtime environment, and data.
An IaaS service allows organizations to purchase resources as needed. Naturally, one of the main advantages of this model of work is the exclusion of the “headache”, which is typical for the maintenance and scaling of local computing centers. At the same time, IaaS clients retain control over the infrastructure. Service providers take on low-level infrastructure management tasks (security, load balancing, backup, etc.).
Notable players in the IaaS market
DigitalOcean
An American company that is a popular provider of cloud infrastructure for developing software for various tasks. Among the main offers of the service: Droplets (virtual machines), Kubernetes container management system, Cloudways cloud hosting, infrastructure for creating, deploying and scaling applications, databases.
Amazon EC2
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud is a service from the AWS (Amazon Web Services) line. It is a popular solution for developers and organizations that need a flexible and stable infrastructure for building software products and applications. Amazon EC2 helps you quickly load and scale your servers to meet your current compute needs. A web service allows you to develop and maintain applications with security and fault tolerance.
Azure Virtual Machines
Azure Virtual Machines is a service from the Microsoft Azure cloud service family. This IaaS solution provides scalable computing power and infrastructure for developing, testing, running, and scaling applications. With this service, you can quickly and cost-effectively create Linux and Windows virtual machines. Virtual Machines allow companies to delegate workloads to Azure infrastructure, run applications and high-performance computing in the cloud.
Google Compute Engine
Compute Engine is an IaaS solution for creating and running virtual machines in the cloud. This service is part of the Google Cloud platform. The service allows you to quickly get started using ready-made and customized configurations. Also, users can create a customized development environment that will best suit the tasks. Compute Engine offers confidential computing, automated automation recommendations, and spot VMs for batch tasks.
What is the Difference Between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
Let's recap all of the above. SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are models for delivering applications, computing power, and infrastructure over the Internet. Running cloud solutions requires a specific stack of technologies, components, and resources. This set, as a rule, consists of the following components: application/program, data, runtime environment, middleware, operating system, virtualization system, servers, data centers, cloud network.
The main difference between the IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS models lies in the way tasks and responsibilities are distributed between the client and the service provider. In simple terms, who is responsible for what. Let's look at this visually – IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS.
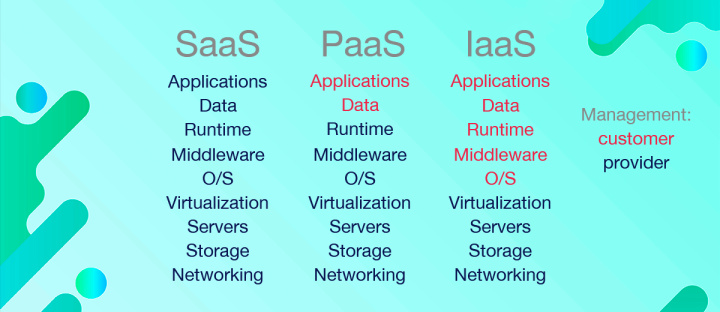
Thus, in the SaaS model, the client does not affect the software product and its operation in any way. The user gets at his disposal an application for solving specific problems. All responsibility for content, support, security, etc. lies with the provider.
What is the difference between SaaS and PaaS? In the case of the PaaS model, the expansion of the rights and powers of the client is assumed. Customer takes responsibility for developing, testing, deploying and maintaining the application. PaaS is a tool for developers and companies that create cloud services on their own.
The IaaS model further expands the list of tasks that are assigned to the customer. In this case, clients undertake the organization and management of a customized system/platform based on a ready-made infrastructure.
Other Members of the _aaS Family
All cloud services that exist today are usually classified into one of the 3 models described above. However, some divide them by more narrowly specifying the type of service. Their number is steadily growing, supplemented by new types of services. In this regard, the term EaaS ("Everything as a Service") or, alternatively, XaaS appeared.
The XaaS model compares favorably with the classic ways of IT business modernization. According to it, almost any technology is simply rented from the provider. In this way, you can rent equipment (“hardware”), data center space, storage space, platforms, IT facilities, individual libraries, computer programs, and even specialist man-hours. With such a model, there are almost no limits to the possibilities.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with several interesting _aaS models:
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
DaaS (“Desktop as a Service”) is a turnkey virtual office. The workspace is represented by virtual stations located in the cloud with an operating system, all the software necessary for work and dedicated technical parameters. All this makes it possible to work in any place where there is an Internet connection. Such a service has flexible individual settings and allows you to adjust it to certain tasks or positions of employees. The remote workplace is quickly deployed and configured on the employee's device directly from the cloud. It is deployed, maintained and managed by a DaaS provider.
DaaS is ideal for many teams working remotely, as well as companies whose employees are located in different cities and countries. It allows you to significantly save the budget of enterprises, reducing several categories of costs at once: from electricity bills to capital costs.
Examples of DaaS providers: Amazon WorkSpaces, Desktone.
Storage as a Service (StaaS)
Storage as a Service (StaaS) is a provider-managed service that provides a customer with access to a virtual storage platform. It allows you to place files and folders in an external type of storage – the cloud, and also offers ample opportunities for working with data (compression, deduplication, instant screenshots, and so on).
Examples of StaaS providers: Dell EMC, Google Drive and Google Cloud, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Amazon Web Services (AWS), IBM, Microsoft Azure, NetApp, Oracle Cloud, Arcserve, Box.
Security as a Service (SECaaS)
Security as a Service (SECaaS) is a cloud service model that guards your cybersecurity by providing protection for the client's IT infrastructure from the cloud. "Physically" it looks like software that is in the provider's cloud. Such a service is built into the user's infrastructure and protects it from unauthorized cyber intrusions. It provides strong data encryption and email security, is responsible for network security and data loss prevention, provides continuous monitoring services, disaster recovery and others.
One of the benefits of SECaaS is dynamic scalability. The client can
install protections on their entire production infrastructure, as well
as safe on deploying and maintaining their security system. Due to
the flexibility of the payment system, the user can choose only those
functions that need.
Examples of SECaaS providers: Continuous Monitoring, Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BC/DR or BCDR), Email Security, Antivirus Management, Spam Filtering, Identity and Access Management (IAM), Network Security, Intrusion Protection.
Accountancy as a Service (AaaS)
Accountancy as a Service (AaaS) is an innovative model for providing
accounting services to a client. It involves the user renting the
resources of a web-based accounting platform, which is located in the
cloud of the service provider. At the heart of the AaaS model is the
attitude to accounting as a modular service scheme, instead of the
classic office system.
Today, to maximize the automation of accounting, AI tools are
being actively introduced and used. Combining it with AaaS will allow
you to get a new generation of accounting, radically different from the
traditional services provided by accounting firms some 3–4 years ago.
Examples of AaaS providers: Lavoie CPA, Local Accountant, FreshBooks, QuickBooks, Xero, Pabbly, Wave, Sage 50cloud.
Summing Up
The market entry and rapid development of cloud services has given many
service providers a tangible boost that has prompted them to make
fundamental changes in their business strategies. Apparently, over
the next ten years, the development, and improvement of cloud computing
will remain just as active. This is already evident in the growing
expectations of users inspired by the progress. Therefore, cloud service
providers will have to search for new ideas and solutions to retain
existing and attract new customers.
According to the forecasts of the leading research and consulting company Gartner Inc., in 2023 user spending on cloud services
worldwide will increase by 20.7%. They will pay $591.8 billion (for comparison: in 2022 – $490.3
billion). Given the ongoing process of digital transformation of
companies and the tendency of their leadership to shift the workload to
cloud platforms, analysts note that the speed of development of the XaaS
industry will show strong growth next year.
Do you want to achieve your goals in business, career and life faster and better? Do it with ApiX-Drive – a tool that will remove a significant part of the routine from workflows and free up additional time to achieve your goals. Test the capabilities of Apix-Drive for free – see for yourself the effectiveness of the tool.

